Introduction
The automotive industry has witnessed a revolutionary shift in recent years with the emergence of autonomous vehicles. This transformative technology has the potential to redefine transportation as we know it, promising enhanced safety, efficiency, and convenience. At the heart of this evolution lies the critical component of terrain sensing and adaptation. As autonomous vehicles navigate various landscapes and environments, the ability to discern and respond to different terrains becomes paramount. In this blog, we will delve into the intricacies of patenting autonomous vehicle terrain sensing and adaptation, exploring the key considerations, challenges, and strategies for securing intellectual property in this rapidly evolving field.
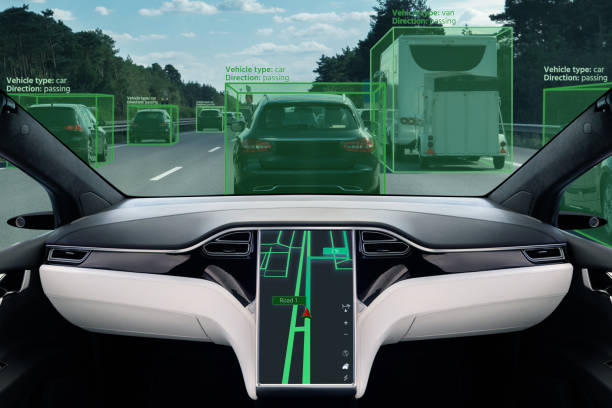
Understanding Autonomous Vehicle Terrain Sensing
Autonomous vehicle terrain sensing is a fundamental component that enables self-driving vehicles to navigate diverse environments and terrains with precision and safety. This technology involves a sophisticated integration of various sensors, data processing algorithms, and intelligent systems that work in tandem to perceive, interpret, and respond to the surrounding terrain conditions. The primary goal of terrain sensing is to provide the autonomous vehicle with real-time information about the immediate environment, enabling it to make informed decisions and adjustments to ensure a smooth and safe driving experience.
Key Components of Autonomous Vehicle Terrain Sensing
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): LiDAR technology plays a crucial role in generating high-resolution 3D maps of the vehicle’s surroundings. By emitting laser pulses and measuring the time it takes for the light to reflect off surrounding objects, LiDAR sensors can create detailed point clouds that represent the terrain, obstacles, and other vehicles in the vicinity. This data is then processed to create a comprehensive understanding of the terrain’s features and characteristics.
- Radar Systems: Radar systems are instrumental in detecting and tracking objects in the vehicle’s vicinity, including other vehicles, pedestrians, and potential obstacles. By utilizing radio waves, radar sensors can accurately assess the distance, speed, and trajectory of various objects, thereby facilitating the vehicle’s ability to anticipate and respond to dynamic changes in the environment.
- Cameras: Vision-based systems, including cameras and image processing algorithms, are essential for capturing and analyzing visual information from the surroundings. Cameras enable the vehicle to identify road signs, traffic signals, lane markings, and other critical visual cues necessary for making informed navigation decisions. Advanced image processing techniques help in object detection, classification, and recognition, enhancing the vehicle’s ability to understand complex visual scenarios.
- GPS and Mapping Data: Global Positioning System (GPS) technology, coupled with detailed mapping data, provides autonomous vehicles with accurate location information and precise mapping of the surrounding terrain. This allows the vehicle to determine its exact position, plan optimal routes, and anticipate upcoming changes in the terrain, such as elevation, curves, and intersections.
- Sensor Fusion and Data Processing: Autonomous vehicles employ sensor fusion techniques to integrate data from multiple sensors, enabling a holistic perception of the surrounding environment. Advanced data processing algorithms analyze the sensor data in real-time, facilitating the detection of potential hazards, identification of optimal driving paths, and adaptive decision-making based on the terrain conditions.
The Integration of Terrain Sensing with Vehicle Control Systems
Autonomous vehicle terrain sensing is intricately linked with the vehicle’s control systems, including steering, acceleration, braking, and overall navigation. The data obtained through terrain sensing technologies is processed and utilized by the vehicle’s control algorithms to make instantaneous adjustments, ensuring optimal performance and safe operation in diverse terrains. By continuously monitoring the terrain and adapting to changes in the environment, autonomous vehicles can navigate smoothly, avoid collisions, and optimize energy efficiency, thereby enhancing passenger safety and comfort.
Crucial Factors in Patenting Terrain Sensing Technology
Securing a patent for terrain sensing technology is a multifaceted process that requires a comprehensive understanding of the intellectual property landscape, technological innovations, and legal intricacies. To successfully patent terrain sensing technology for autonomous vehicles, several crucial factors must be carefully considered and addressed. These factors significantly influence the patentability and commercial viability of the technology. Key considerations include
Novelty
Novelty is a fundamental criterion for patentability. To obtain a patent, the terrain sensing technology must demonstrate a unique and original approach that sets it apart from existing solutions. Conducting a thorough prior art search is crucial to identify any similar or related technologies that might impact the novelty of the invention. Emphasizing the novel aspects of the terrain sensing technology, such as innovative sensor integration, advanced data processing algorithms, or unique applications in autonomous vehicle navigation, is essential for securing a strong patent.
Non-obviousness
In addition to being novel, the terrain sensing technology must also exhibit non-obviousness. This means that the solution should not be an obvious extension or combination of existing technologies or methods. Demonstrating how the proposed technology involves inventive steps or a significant departure from conventional practices is critical in establishing its non-obvious nature. Highlighting the specific technical challenges or complexities that the terrain sensing technology overcomes can strengthen the argument for non-obviousness and bolster the patent’s validity.
Industrial Applicability
A key aspect of patentability is the industrial applicability of the terrain sensing technology. For autonomous vehicles, the technology must demonstrate practical and tangible utility in enhancing the vehicle’s navigation, safety, and adaptability to various terrains and environmental conditions. Providing empirical evidence, experimental results, or real-world use cases that highlight the benefits and functionality of the terrain sensing technology within the context of autonomous driving is crucial in establishing its industrial applicability.
Technical Advancement
Patent examiners often assess the level of technical advancement or innovation that the terrain sensing technology brings to the field of autonomous vehicles. Highlighting the technological advancements, such as improved accuracy, enhanced data processing speed, integration with artificial intelligence, or the ability to handle complex terrain scenarios, can significantly strengthen the patent application. Clearly articulating how the technology represents a significant leap forward in autonomous vehicle navigation and safety can substantiate its technical advancement and patentability.
Patent Drafting and Claims
The drafting of the patent application and the formulation of precise, well-defined patent claims are critical for successfully securing a patent for terrain sensing technology. The patent application should provide a comprehensive and detailed description of the terrain sensing technology, including its components, functionalities, and technical specifications. Clear and specific patent claims that define the scope and boundaries of the invention, highlighting the unique features and aspects of the terrain sensing technology, are essential for effectively protecting the intellectual property rights associated with the invention.
By meticulously addressing these crucial factors and presenting a compelling case for the novelty, non-obviousness, industrial applicability, technical advancement, and patent drafting precision of the terrain sensing technology, patent applicants can significantly enhance their prospects of securing valuable patents in the burgeoning field of autonomous vehicle technology. Collaborating with experienced patent attorneys and intellectual property experts can provide invaluable guidance and support in navigating the intricate patenting process and maximizing the protection and commercial potential of terrain sensing innovations.

Challenges in Patenting Autonomous Vehicle Terrain Sensing
Patenting autonomous vehicle terrain sensing technologies presents a unique set of challenges, owing to the rapid advancements in the field, the complex nature of the technology, and the intricacies of intellectual property law. Successfully navigating these challenges requires a comprehensive understanding of the evolving landscape of autonomous vehicles, coupled with a strategic approach to addressing the specific hurdles associated with patenting terrain sensing innovations. Key challenges in patenting autonomous vehicle terrain sensing include:
1. Rapid Technological Evolution
The autonomous vehicle industry is characterized by rapid and continuous technological evolution. New sensor technologies, advanced data processing algorithms, and innovative navigation systems are constantly being developed and integrated into autonomous vehicles. Keeping pace with these rapid advancements while simultaneously securing patents for cutting-edge terrain sensing technologies can be challenging. Patent applicants must demonstrate that their terrain sensing solutions represent a significant leap forward in the field, incorporating novel methodologies or addressing critical limitations in existing technologies.
2. Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape in the autonomous vehicle industry is fiercely dynamic, with numerous companies and research institutions actively pursuing innovations in terrain sensing. Patent applicants must navigate a crowded field of competitors seeking to secure intellectual property rights for similar or related technologies. Conducting comprehensive patent searches and competitive analyses to identify existing patents and innovations is crucial for developing a terrain sensing technology that stands out in the competitive landscape and offers distinct advantages over existing solutions.
3. Legal Ambiguities and Interpretations
Patent laws and regulations related to autonomous vehicles and terrain sensing technologies can be ambiguous and subject to interpretation. As the legal framework continues to evolve alongside technological advancements, patent applicants must navigate complex legal nuances and ensure that their patent applications comply with the latest legal requirements and standards. Working closely with experienced intellectual property attorneys who specialize in autonomous vehicle technology can help navigate the intricacies of patent law and ensure that patent applications adhere to the relevant legal provisions.
4. Interdisciplinary Nature of Technology
Autonomous vehicle terrain sensing technologies often involve an interdisciplinary blend of engineering, computer science, artificial intelligence, and data analytics. Patent applicants must effectively communicate the technical complexities and interdisciplinary aspects of their terrain sensing innovations to patent examiners, who may have varying levels of expertise in different technical domains. Clearly articulating the technical intricacies, the practical applications, and the potential industrial impact of the terrain sensing technology is crucial for overcoming potential challenges related to the interdisciplinary nature of the technology.
5. Patent Filing Strategy
Developing a comprehensive and effective patent filing strategy is essential for maximizing the protection and commercial value of autonomous vehicle terrain sensing technologies. Determining the appropriate timing for filing patent applications, selecting the right jurisdictions for filing, and formulating robust patent claims that encompass the key aspects of the technology are integral components of a successful patent filing strategy. Engaging in strategic patent portfolio management, including the filing of provisional patents, international patents, and continuation applications, can help secure comprehensive protection for terrain sensing innovations and provide a competitive advantage in the market.
By proactively addressing these challenges and adopting a strategic approach to patenting autonomous vehicle terrain sensing technologies, patent applicants can position themselves for success in the competitive landscape of autonomous vehicle innovation. Emphasizing the unique features and benefits of the terrain sensing technology, leveraging interdisciplinary expertise, and collaborating with experienced legal and technical professionals can significantly enhance the prospects of securing valuable patents and establishing a strong intellectual property position in the rapidly evolving field of autonomous vehicles.
Strategies for Patenting Autonomous Vehicle Terrain Sensing and Adaptation
- Comprehensive Patent Search: Before filing a patent application, conducting a comprehensive patent search is essential to identify existing patents and ensure that the proposed technology meets the criteria for novelty and non-obviousness. This process aids in refining the patent application to emphasize its unique aspects.
- Collaborative Research and Development: Establishing collaborations with research institutions, universities, and industry experts can significantly strengthen the patent application. Collaborative efforts often lead to the development of groundbreaking technologies that stand a better chance of securing patents.
- Constant Innovation and Iteration: Continuous innovation and iteration are imperative in the autonomous vehicle domain. Engaging in research and development activities to enhance existing terrain sensing technologies and adapt to emerging trends can bolster the patent portfolio and solidify the position of the patent holder in this competitive landscape.
Conclusion
Patenting autonomous vehicle terrain sensing and adaptation is a multifaceted process that demands a thorough understanding of the technology, legal intricacies, and industrial applications. As the automotive industry hurtles towards a future dominated by autonomous vehicles, securing patents for terrain sensing technologies remains a critical step in safeguarding intellectual property and fostering innovation. By embracing a proactive approach to research and development, collaborating with industry peers, and navigating the legal complexities with precision, stakeholders can pave the way for a transformative future in autonomous vehicle technology.Is this conversation helpful so far?


